
Significance of the landscape
The Medak Forest Division is located in the central-west part of Telangana State. It has a semi-arid, hot, and dry climate. The forest division and administrative district boundaries are coterminous and form part of the Deccan Plateau, with undulating terrain. Major crops grown are paddy rice, maize, jowar, castor, sunflower, chilies, and pulses. The Manjira River, a tributary of the Godavari River, flows through the district and is the main source of water for the twin cities of Hyderabad and Secunderabad. The river supplies irrigation in the areas around the landscape. Large portions of recorded forest area are open forest, shrub forest, and areas devoid of trees.
Medak has large tracts of contiguous forest and have a high potential for planning trees outside forest (TOF). The district is covered under the Telanganaku Haritha Haram Program, a flagship programme of the state government, which was launched in 2015 to increase the green cover of the state from 24 percent to 33 percent.
The Pocharam Wildlife Sanctuary is located about 100 km from Hyderabad and 18 km from Medak. The sanctuary is 130 km2 and overlaps with neighboring Kamareddy District. Two deer breeding centers (DBCs) have been established in Pocharam Wildlife Sanctuary.
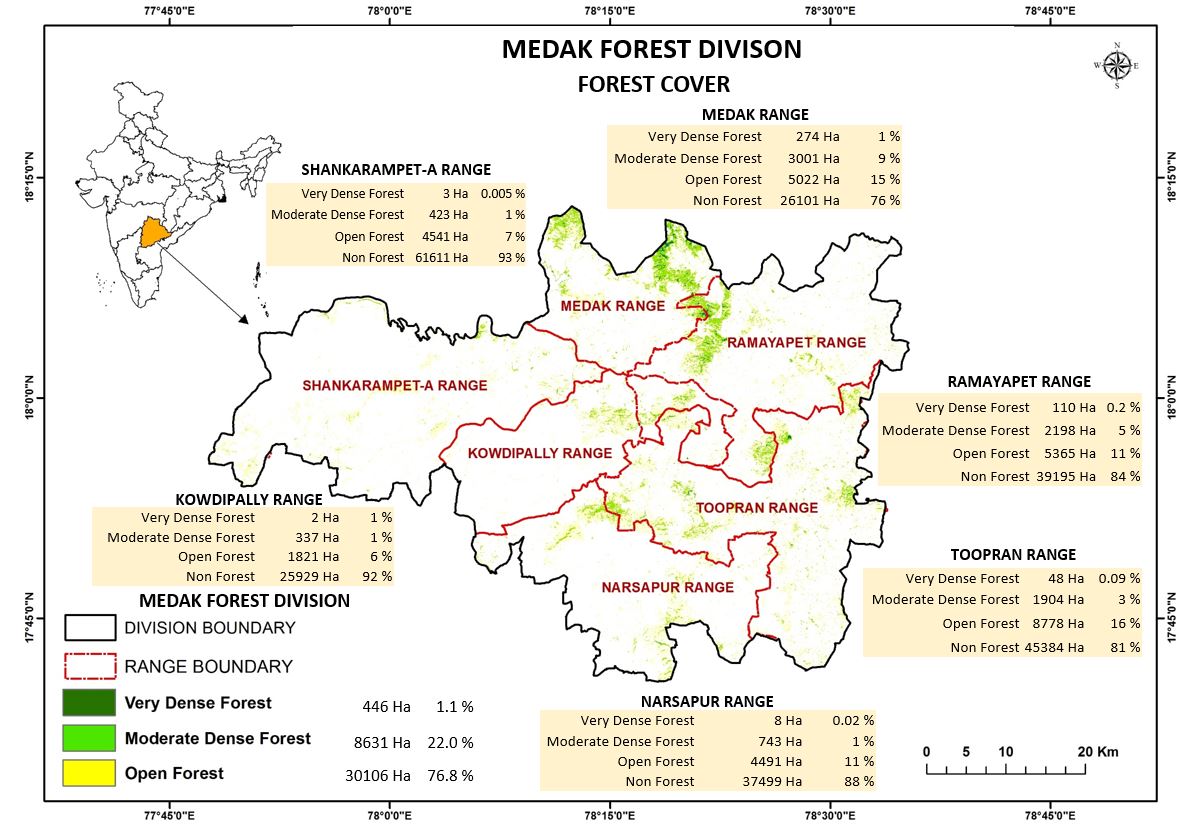
Forest Cover
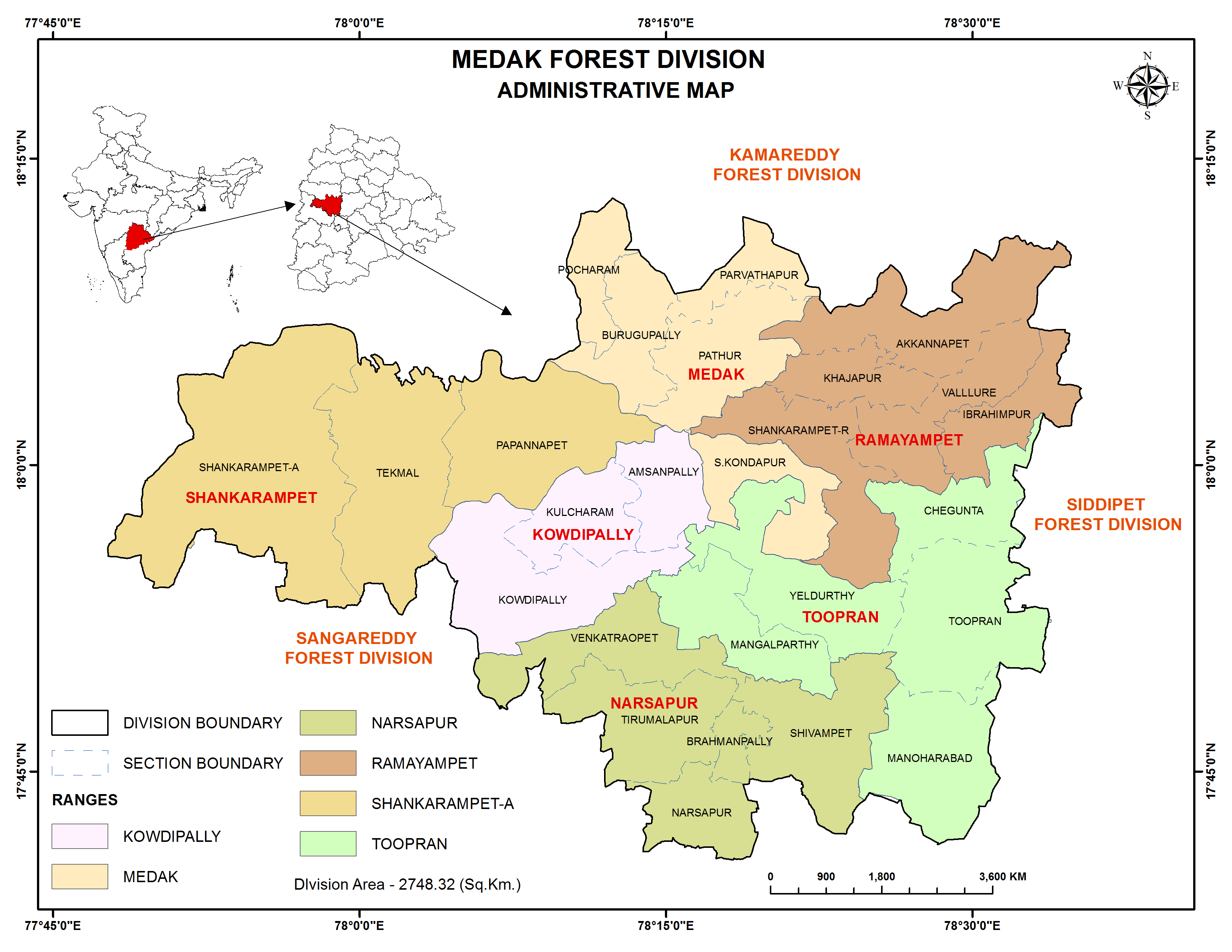
Administrative Map
Ecosystem Services in Medak
- Provisioning Services: The provisioning services provided by the ecosystem of Medak Forest are in the forms of fruits, seeds, and medicinal plants for the local population. Fruits include sitaphal, chironji seeds, and medicinal herbs sourced from the forest. The non-timber forest products include teak, neem, mahua, sal, beedi leaves, and grass.
- Regulating Services: Air quality regulation, climate regulation, water regulation (e.g. water conservation, water quality and health maintenance), carbon sequestration all support communities from the enhanced forest with food productivity, pest and disease control, as well as from erosion. Farmers and forest-based communities’ benefit and depend on these services to protect their vegetation cover and topsoil. There are also pollination benefits from the forest both locally as well as regionally.
- Cultural Services: The Medak landscape forests provide the local population with avenues for eco-tourism, as well as spiritual and religious tourism. The landscape contains sacred groves that are protected and worshipped by many communities.
- Supporting Services: The community receives various benefits from the supporting services provided by the Medak landscape. These mainly include provision of biodiversity, soil formation, primary production, and nutrient cycling.
Medak Forest Division (Forest Cover)

Medak Forest Division (Administrative Map)


